Odor is perceived by olfactory receptors in two ways: direct odors via the nose (orthonasal olfaction) or odors that reach the nose via the throat during and after the masticatory act (retronasal olfaction). Current analysis of retronasal odor is typically achieved by the sequential capture of volatile compounds using Tenax tubes and subsequent analysis by a gas chromatography mass spectrometer (GC-MS), which is a time-consuming process. To measure odor leakage on a breath-by-breath basis, a rapid non-invasive method with in vivo measurements is required.
Background
Solution
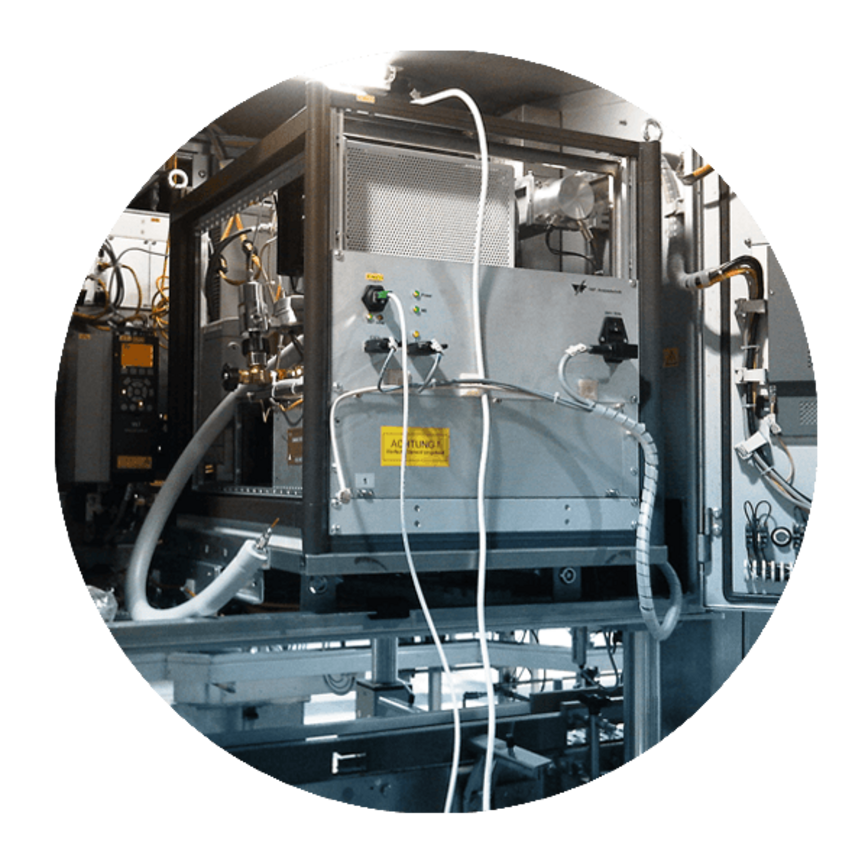
V&F's innovative IMR mass spectrometers are equipped with a gas transfer line that can be inserted into the nasal cavity without causing discomfort. This method allows measurements of odor molecules released with each breath. Chewing gum aroma (menthol, limonene) or coffee aroma (furfural, 2,3-butanedione) can be measured continuously to determine in vivo objective time profiles of aroma intensity that can be compared to subjectively perceived odor intensity and sensory evaluation by the subject.
Advantages
V&F provides mass spectrometers for use in the flavor industry. Ion Molecular Reaction Mass Spectrometry (IMR-MS) provides a highly selective and highly sensitive technology to measure volatile organic compounds in real time. IMR-MS represent compact analytical instruments for the flavor industry, which can be used for measurement tasks in vivo (nasal cavity) as well as in vitro (gas chamber).
Reference clients (excerpt)