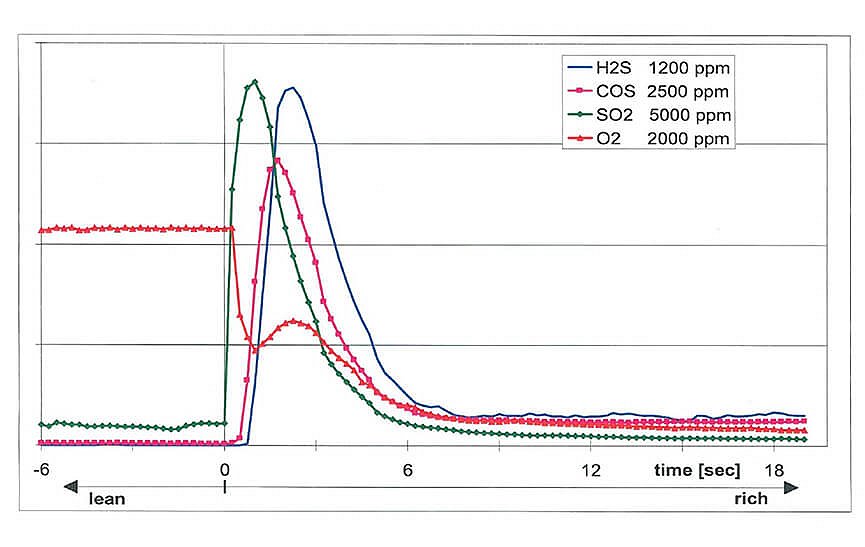
The SO2, COS, and H2S sulfur components are formed in the combustion engine during the combustion of fuel impurities in the cylinder. These are powerful catalyst poisons as well as the nuclei of particulate formation. The standard desulfation mechanism is a rich hydrocarbon load and hydrogen feed to the catalyst. This applies to nitrogen traps, particulate filters, and in general to all catalytic devices in exhaust gas treatment. To develop and fine-tune these types of strategies for desulfation, instrumentation is required that can accurately distinguish between SO2, COS and H2S while providing both sensitivity down to low ppm ranges and rapid response times.
Background
Solution
V&F IMR (Ion Molecular Reaction) technology within the V&F AirSense mass spectrometer can measure all sulfur components with the required sensitivity and selectivity. Inlet pressure regulation (0 to 5 bar), particulate filters, and a heated transfer capillary are additional features required for exhaust emissions measurement. A variety of interface options, such as AK protocol, guarantee easy implementation in a test bench environment.
Advantage
Known technologies such as FTIR cannot measure certain sulfur mixtures such as SO2. They may also encounter interference when determining H2S. IMR technology, with its rapid response times of <200 ms, allows users to create detailed time profiles of the desulfurization process to more accurately measure effectiveness. The V&F AirSense's robust and compact design combined with low maintenance makes it an excellent tool for more demanding exhaust gas measurement applications.