Aside from sulfur, NO is one of the most undesirable substances in exhaust gas after-treatment. It is formed by the splitting of NO2 in the cylinder and a chemical reaction with O2 at high cylinder temperatures. Suppression of NOx formation, like reduction in exhaust after-treatment, is the main task of engine and catalyst developers. Whatever the strategy, be it, for example, low-temperature combustion, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), post-injection to form enough HC for catalytic reduction, or SCR technology with decomposition of urea into ammonium molecules, to achieve optimization under volatile conditions these highly dynamic and heavily temperature-dependent reactions require the rapid measurement of a wide range of components.
Background
Solution
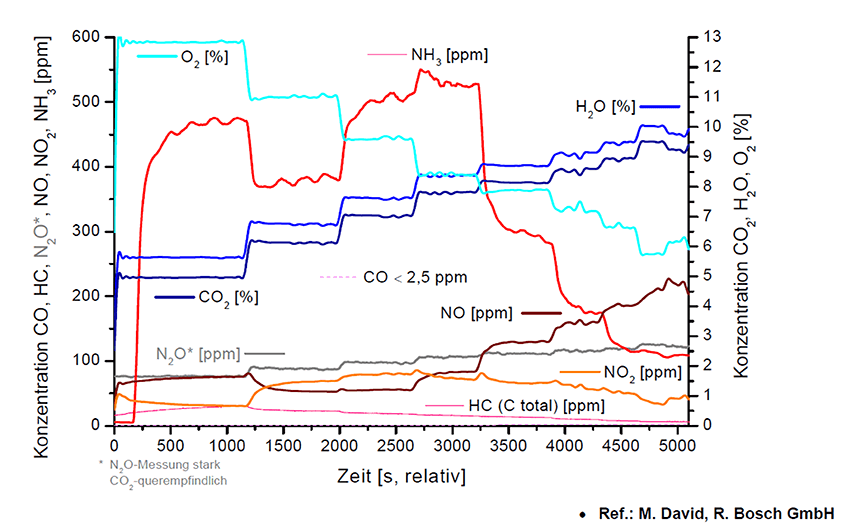
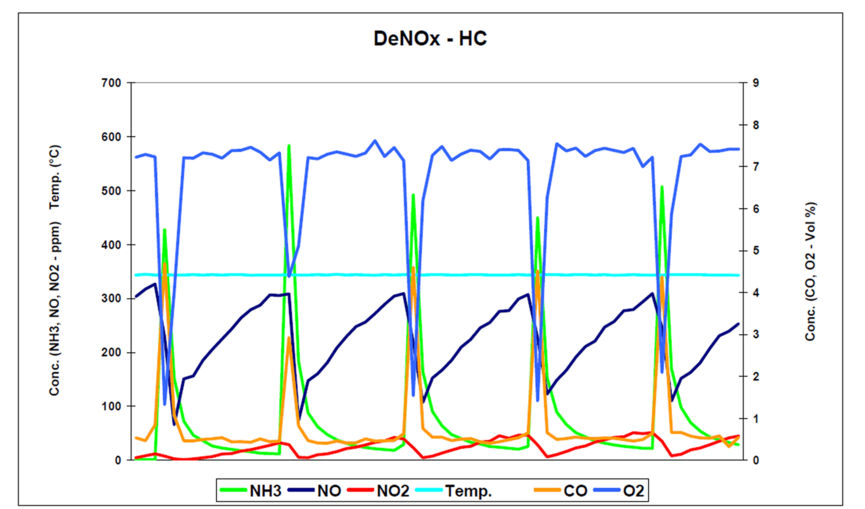
The patented V&F IMR technology (Ion Molecule Reaction) can identify all significant nitrogen components, i.e. NO, NO2, NH3, etc. with the required measurement speed. In addition, other relevant molecules can also be measured for the determination of the DeNOx process on nitrogen traps such as O2. The V&F ComboSense also facilitates the detection of N2O at low ppm levels. Inlet pressure regulation (0 to 5 bar), particulate filters, and a heated transfer capillary are additional features required to measure exhaust emissions. A variety of interface options, such as the AK protocol, guarantee easy integration into a test bench environment.
Advantages
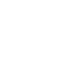
DeNOx concepts for on-road vehicles require a strategy that is more complex than simply controlling hydrocarbon (HC) and CO emissions. HC and CO formation is directly related to the air-fuel ratio, which is clearly determined by fuel inlet, air volume, and lambda value. NO formation is related to the air-fuel ratio, flame temperature, and cylinder pressure. FTIR instruments are limited in their gas response times and low determination levels, especially in diluted gases (CVS = continuous volumetric sampling). V&F's IMR technology allows measurement speeds of up to 10 Hz and limits of quantitation (LOQ) in the low ppb range. The robust and compact design of the V&F instruments combined with low maintenance makes them an excellent tool for more demanding applications in the field of exhaust gas measurements.