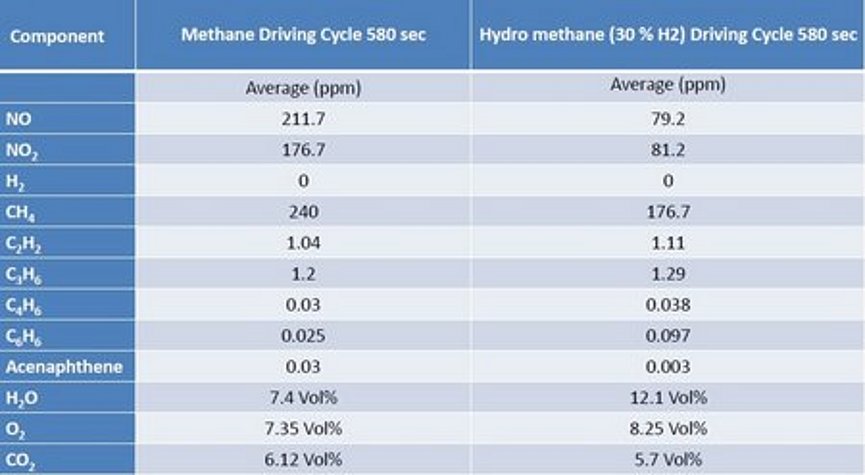
Hydrogen can be added to the methane to improve the emission properties of natural gas engines. Mixtures with up to 30 vol% hydrogen and approximately 70 vol% methane are usually referred to as hydromethane. The use of hydromethane improves the combustion properties of the engines and results in lower NOx emissions. In addition, the formation of particulate matter is reduced, as can be seen from the decrease in precursor molecules such as acenaphtene - a cyclic hydrocarbon. To precisely compare the emission profiles of natural gas and hydromethane in non-stationary driving cycles, a powerful V&Fanalyzer is needed that can determine the inorganic substances such as NO, NO2, and other organic compounds.
Background
Solution
The patented IMR technology within V&FAirSense can determine all compounds concerned. Time profiles of organic and inorganic emissions can be created with one measurement setup. Furthermore, the IMR technology enables the detailed analysis of a number of hydrocarbons, e.g. acetylenes, benzene, or toluene as well as acenathene C12H10). The latter compound is very important in studying particle formation in natural gas engines. A variety of interface options such as the AK protocol guarantee easy integration into the test bench environment.
Advantage
Since measurement systems based on FTIR technology inherently have problems differentiating hydrocarbons > C3, they are not suitable for accurate investigation of organic emissions from natural gas engines. The V&FAirSensemass spectrometer offers great flexibility in terms of component selection. Setups can be quickly edited by the technician, and new molecules of interest added. The V&FAirSense's sturdy and compact design, combined with its low maintenance requirements, makes it an excellent tool for challenging exhaust gas measurement applications.
Reference clients (excerpt)